
Healthcare is one of the most sensitive and essential industries around the globe. As a result, information systems in healthcare are often targeted by cybercriminals. It is a large industry that handles sensitive health data for all individuals worldwide. Healthcare information systems are large networks of hospitals, pharmacies, pathologies, health insurance companies, and pharmaceutical research companies that collect and store sensitive information, also known as Personal Health Information(PHI).
Technology has grown massively, where devices are connected to each other using the Internet of Things(IoT) which has been transformed into the Internet of Everything. We have taken everything for granted from the initial days of transition in technology which has made us ultimately dependent in our daily life. Meanwhile, we are unaware of things happening in the cyber world, specifically in the med-tech world. The blind trust game persists until everyone is safe from cybersecurity incidents. The health information system and medical/healthcare devices are the major concern in the field of cybersecurity. A health information system refers to a system designed to manage healthcare data. This includes systems that collect, store, manage and transmit a patient’s electronic medical record (EMR), a hospital’s operational management, or a system supporting healthcare policy decisions. For example, IT systems like Hospital management systems, Online OPD, Pathology Reporting, Pharmacy systems, etc can be anointed as HIS.
A growing body of research shows that medical devices are vulnerable to attacks due to inherent design flaws and poor cybersecurity practices. Devices like Computed Tomography(CT), Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), X-Ray, and other medical imagery services are targeted by malicious intent users or hackers. Factors like Human error, external access, and misconfiguration make them prone to security loopholes.
A cybersecurity attack on health industry systems can have severe consequences for patients and their families. While security practices are becoming more sophisticated, these criminals are finding new and creative ways to penetrate networks, access sensitive information, or cause damage.
Healthcare organizations face several cybersecurity challenges, including:
1. Malware: Cybercriminals can exploit vulnerabilities in healthcare information systems to install malware that can steal patient or research information or damage critical computer systems and ask for ransom.
2. Data breach: Cybercriminals can use stolen identity information to perpetrate fraud or launch other attacks and sell them over the dark net for financial benefits.
3. Denial of service: Cybercriminals can target healthcare organizations with DDOS (Distributed Denial of Service) attacks that overload systems and cause service disruptions leading to financial loss, higher operational costs, delays in treatment & loss of life.
Since cyberattacks often go undetected for long periods of time, healthcare organizations must have effective strategies in place for detecting these threats early on. There are several cybersecurity solutions available that can help healthcare organizations protect their systems and data. Security attacks on healthcare information systems can shut down the business for days, putting lives at risk due to delayed diagnosis and treatments and vulnerable healthcare devices that could harm human life. The global pandemic taught us how a virus could replicate and shut down businesses and affect the global economy So, as computer viruses can. The world is in the control of someone that can be stealthy and make allies and attack distributively.
I have uncovered that the most critical things are implantable devices in the human body which come with deadly risks. Devices like pacemakers, insulin pumps, deep brain neurostimulators, gastric stimulators, foot drop implants, cochlear implants, defibrillators, etc can be hacked to affect human lives. We are almost okay with a robot performing surgery but never thought about the risks when the robot could be misapplied. Although the technologies like Artificial Intelligence(AI), Machine learning, and deep learning produce clearer medical images for radiologists and can predict possible diseases like cancer, etc in the future days. But everything comes with a price which is “risks” in this case.
The below screenshot provides the post-haste issues in healthcare/medical devices.

The internet is an open place where one can search for literally everything, with the rapid advancement of technology, attackers or cybercriminals are more sophisticated and intelligent. Search engines like Shodan, unlike google /yahoo search, can be used to find the exposed and vulnerable services on the internet. The improper configuration and poor security always make the system vulnerable and opens a door for malicious intent users. Using uncomplicated search queries with Shodan and other search engines, one can access the health care systems exposed to the internet. Such systems include medical imagery solutions, Lifecare support, patient management systems, etc.
For example, here is the X-RAY scanner machine panel exposed on the internet with the default credentials admin/admin.
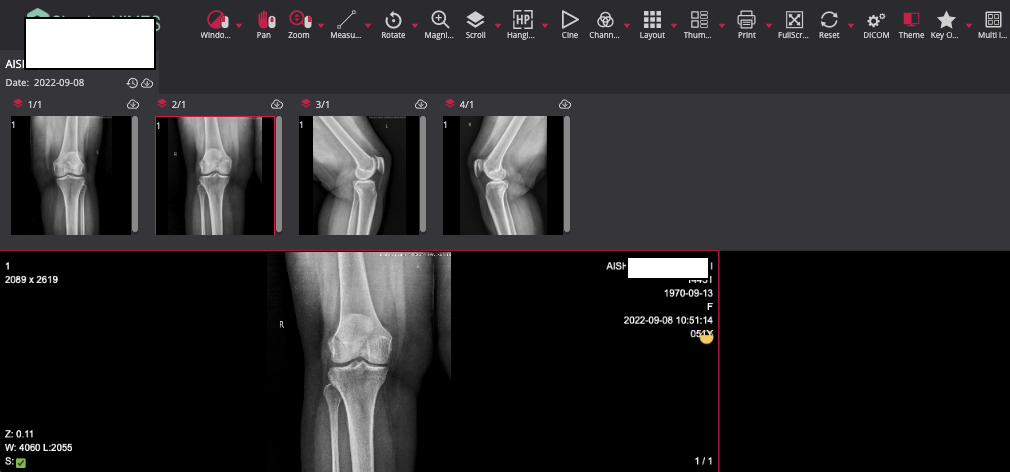
This can be misused by an attacker to add, edit or remove the data from the scanner, which might definitely cause an organization financially, and reputational damage for the worst part and can face a heavy lawsuit, and patient’s data can be altered to harm him/her with a single click.
Furthermore, a simple google dork landed on this page, Printer access in the hospital network disclosing critical information about patients.
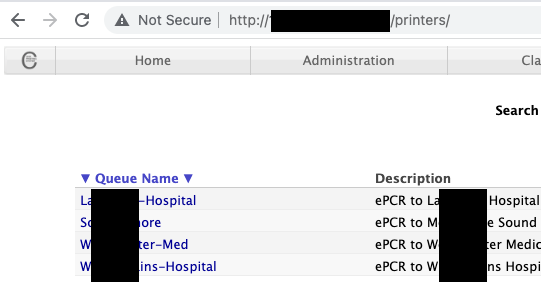
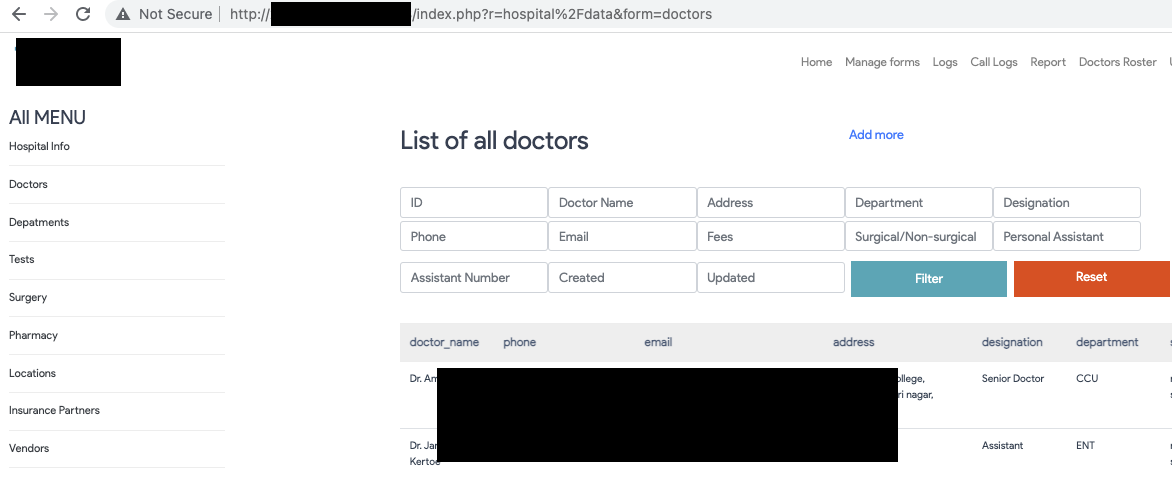
Some emerging concepts like Doctor on Call (DOC), Telemedicine, and online OPD features are essential in the field of medical technology but also come with considerable risks, In most cases, These systems are fully functional but are never observed, configured, and improved in the part of security and risk. IT systems dealing with healthcare data/ PHI are always the first target of cybercriminals or hackers due to the high value of such records on the darknet. Data is actually a perpetual source of energy, Where Personal Health Records(PHI) are essential targets of cybercriminals for attacks like identity theft, scam, lethal attacks, etc. Verimetrix, a cybersecurity firm, published a short article about the trust cost of PHI breach, according to which health data are the most valuable thing sold on the darknet.
Some further risks about medical devices and wearables cybersecurity are explained in a TEDx talk by Stephanie Domas, where she talks about unthought risks in medical devices and their fatal effects on the healthcare of human beings.
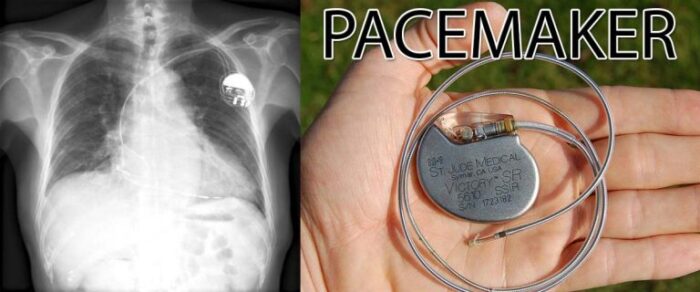
Medical devices are popular as they offer potential benefits for patients and caregivers. Numerous people that rely on pacemakers to keep their hearts beating are at risk of a software vulnerability, glitches, and hackers which could eventually take their lives. A pacemaker is a small electrical battery-operated device surgically implanted in the chest to help control heartbeats. This device uses low-energy electrical pulses to stimulate the heart to beat usually. A cybersecurity researcher hacked her own pacemaker to prove the fact explained in the article.
Nations like the United States and Canada have regulatory control that acts as a governing body providing the guidelines and boundaries about operating, storing, and working with public health data known as HIPAA and PHPA. It also deals with other goals, including combating abuse, fraud, and waste in health insurance and healthcare delivery and improving access to long-term care services and health insurance.
In 2019, Food and Drug Administration issued a remote patient monitoring enforcement policy encouraging healthcare providers to only use devices approved by the FDA and feature robust security features that protect patient data from unauthorized access. Healthcare organizations should implement a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy to protect medical devices and the patient information they collect and store. It is not true that Health equipment or devices approved by Food and Drug Administration(FDA) are secure and unhackable. It is false information, even though health equipment/devices are unhackable, the misconfiguration makes them vulnerable, which could be the entry point for external hackers. To prevent this from happening, it is critical for device manufacturers to develop vigorous security strategies for their devices and implement effective cyber-hygiene measures to prevent security attacks.
The goal of cyber security is to protect patients, healthcare institutions, drug manufacturers, medical research companies, and the industry as a whole from unauthorized access to confidential patient information. To protect patient information, healthcare organizations must use comprehensive security policies and implement appropriate technologies to secure their systems. First, healthcare administrators should educate their staff about common cyber threats and how to avoid them. Healthcare organizations can also identify potential vulnerabilities and threats by conducting regular audits. Once these vulnerabilities are identified, healthcare administrators can implement measures to mitigate them.
Medical device manufacturers should test their devices before release and continuously monitor for vulnerabilities. Security patches should be applied as soon as they are released and tested to ensure there are no adverse effects on the operation of the device. Manufacturers should also develop comprehensive breach response plans to ensure that they can respond to security incidents quickly and effectively.
By understanding how healthcare cybersecurity works and what risks are posed to your organization, you can develop an awareness and preparedness mindset. There are several key steps that an organization should take to protect its systems and information from cyber-attacks.
- Secure the network and information system perimeter.
- Implement strong authentication and access control policies.
- Third-party risk assessment.
- Develop an incident response plan.
- Monitor the system for suspicious activity.
- Identify and classify different cyberattack scenarios.
- Assimilate risk management practices.
- Implement an appropriate cybersecurity governance structure.
It is no secret that healthcare organizations are some of the most targeted worldwide, Let’s hope for the best and prepare for the worst. A preparedness mindset is a key to protecting yourself and your loved ones from healthcare cybersecurity threats.